In the realm of linguistics, the concept of “diminutive” holds a special place, capturing the essence of how language can convey subtle nuances of meaning. This fascinating linguistic feature allows speakers to express affection, familiarity, or even smallness through specific word forms. By adding prefixes or suffixes, diminutives transform ordinary words into endearing or playful variations that resonate with listeners.
Understanding diminutives enriches one’s grasp of language and culture, revealing how different societies express tenderness or intimacy. Whether it’s a child’s name or a beloved pet, diminutives create a sense of closeness that transcends mere words. Dive into the world of diminutives and discover how they shape communication in everyday life.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Dinituve
Diminutive forms in language serve crucial functions. These forms express affection, familiarity, or smallness, modifying ordinary words into more endearing variations. Speakers create diminutives by adding specific prefixes or suffixes to base words, tailoring communication to convey warmth and intimacy.
Diminutives manifest in various languages, reflecting cultural nuances. For example, in English, suffixes like “-y” or “-ie” transform names into more affectionate forms, such as “Johnny” from “John” or “Kathy” from “Katherine.” In Spanish, diminutives often use the endings “-ito” or “-ita,” changing “perro” (dog) into “perrito” (little dog).
Understanding diminutives enhances one’s appreciation of language’s richness. They not only modify meanings but also foster connection among speakers. In contexts like family dynamics, pet names, or playful exchanges, diminutives play a vital role, contributing to a shared sense of intimacy and understanding within different cultures.
Chemical Properties of Dinituve
Dinituve exhibits distinct chemical properties that are essential for understanding its behavior in chemical contexts. Key aspects include its molecular structure and reactivity characteristics.
Molecular Structure
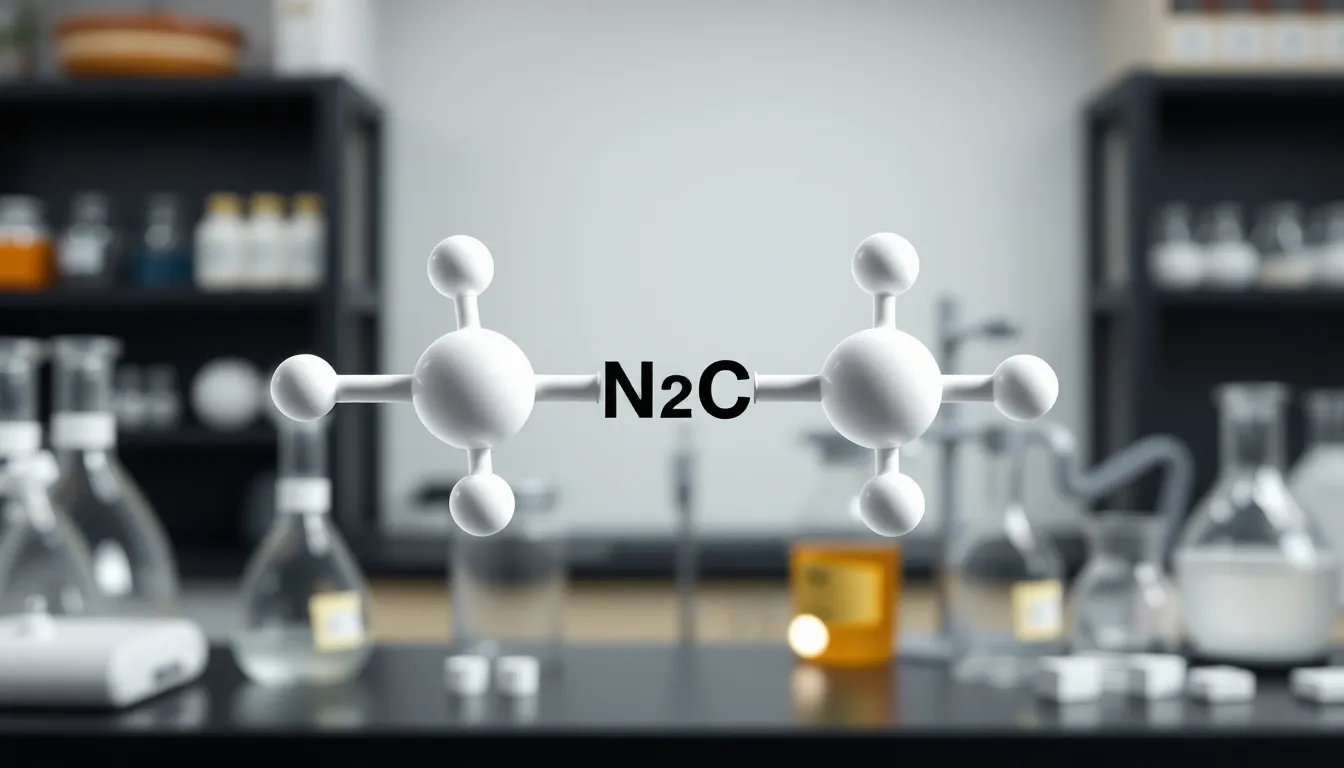
Dinituve consists of two nitrogen atoms bonded to a central carbon atom, forming a linear arrangement. The molecular formula, represented as N₂C, indicates a balance of electron sharing among the atoms. This configuration contributes to its stability, with the nitrogen atoms exhibiting a triple bond to each other, resulting in a strong intermolecular force.
Reactivity Characteristics
Dinituve demonstrates notable reactivity when exposed to various environmental conditions. It readily engages in oxidation reactions, especially upon contact with oxygen, leading to the formation of nitrogen oxides. It also reacts with metals, yielding stable compounds that are significant in industrial applications. Temperature increases can accelerate its decomposition, emphasizing the importance of controlled storage and handling practices.
Applications of Dinituve
Dinituve has several key applications in industrial and research settings. Its unique chemical properties and reactive nature make it valuable across various fields.
Industrial Uses
Dinituve finds extensive use in the production of fertilizers and explosives. Primarily, it acts as a nitrogen source in fertilizers, promoting plant growth by enhancing nitrogen content in soil. Industries utilize dinituve to manufacture ammonium nitrate, an essential component in agricultural fertilizers. Additionally, dinituve’s reactivity contributes to its role in the explosive sector, where it forms stable compounds crucial for controlled detonations. Its applications extend to the production of pharmaceuticals, where dinituve is involved in synthesizing nitrogen-containing compounds, expanding creative solutions in drug manufacturing.
Research and Development
Dinituve plays a significant role in scientific research and development. Researchers study its reactivity patterns to develop new materials and chemical processes. Its molecular structure makes it an interesting subject for academics focusing on nitrogen chemistry and its implications in environmental science. Studies explore the use of dinituve in catalytic processes and energy storage technologies, highlighting inventive approaches for sustainable practices. Collaboration between industry and academia continues to drive innovations involving dinituve, fostering advancements in both chemical engineering and material science.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Dinituve’s safety profile and environmental implications are crucial for its industrial use and research applications. Understanding its toxicity and adherence to environmental regulations ensures responsible handling and minimizes risks.
Toxicology Studies
Toxicology studies indicate that dinituve exhibits low acute toxicity in mammals. Research shows that exposure to high concentrations can lead to respiratory irritation and neurological effects. Chronic exposure assessments reveal potential reproductive and developmental risks, necessitating careful consideration during usage. Protocols for safe handling include using personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and masks, to mitigate exposure risks. Regular health monitoring for workers in industrial settings emphasizes the importance of maintaining safety standards to minimize adverse health effects.
Environmental Regulations
Environmental regulations governing dinituve focus on emission limits and safe disposal methods. Regulatory bodies, like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), classify dinituve as a substance requiring careful management to prevent environmental contamination. Compliance with guidelines ensures that emissions don’t exceed permissible levels. Additionally, manufacturers must follow proper waste disposal protocols to address potential risks of soil and water contamination. Emphasizing sustainable practices and adhering to regulations helps mitigate dinituve’s environmental footprint.
Conclusion
Diminutive forms enrich language by fostering intimacy and affection while dinituve plays a crucial role in various industrial applications. Understanding both concepts highlights the intricate connections between language and chemistry. As society continues to evolve, so will the ways in which diminutives are used and the innovations surrounding dinituve. Embracing these elements not only enhances communication but also supports advancements in sustainable practices. Awareness of their significance can lead to deeper appreciation and responsible use within cultural and industrial contexts.